上周六,,兩名美國宇航員搭載SpaceX的獵鷹9號火箭,,從佛羅里達州卡納維拉爾角發(fā)射,飛向國際空間站,。這是人類歷史上的首次商業(yè)載人航天發(fā)射。
道格拉斯?赫爾利和羅伯特?本肯也是自2011年7月美國航天飛機退役后第一批從本土搭載國產(chǎn)火箭和飛船前往空間站的宇航員,。
此次由美國國家航空航天局(NASA)出資支持的任務(wù)將啟動太空私有化的下一個主要階段,。未來將可能建造一個私人空間站,并在地球以外創(chuàng)建私人任務(wù),。
美國東部時間上周日上午10點16分,,赫爾利和本肯抵達國際空間站,并將航天器與空間站的端口對接,。該飛船的對接機構(gòu)在飛越中國北部和蒙古時連接到該節(jié)點,。2014年,美國宇航局委托兩家私營公司——航空巨頭波音公司和埃隆?馬斯克領(lǐng)導的SpaceX公司,,制造能夠?qū)⑷祟愡\送到國際空間站的運載工具,。從某種程度上說,波音公司落后于其競爭對手SpaceX,,但如果能解決星際飛船艙的故障問題,,它的首次飛行任務(wù)預計將在明年完成。
下面讓我們通過照片,,感受這個歷史上的里程碑時刻,。(財富中文網(wǎng))
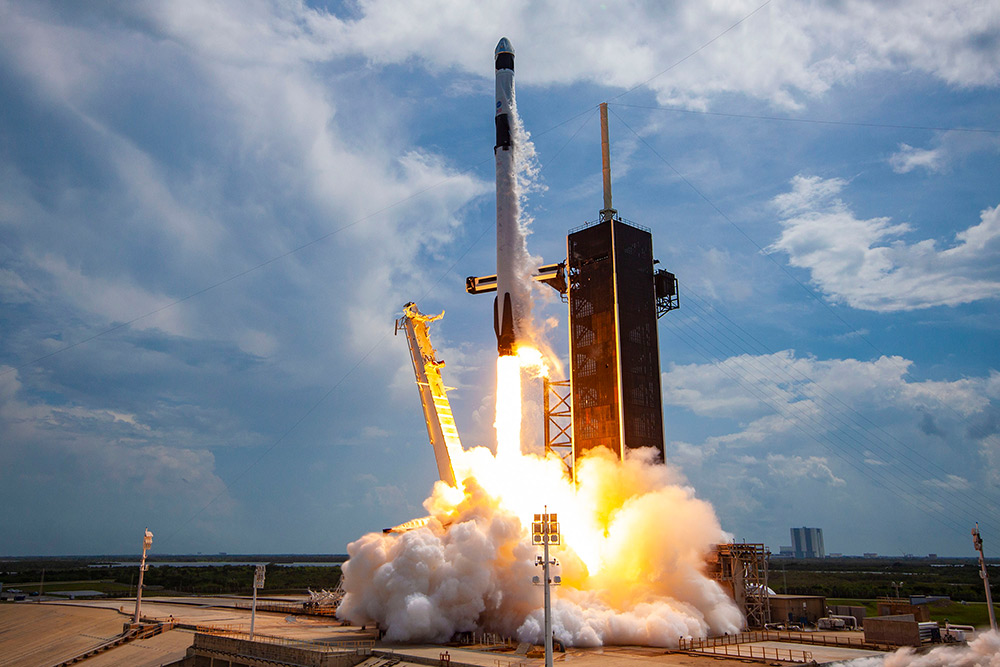
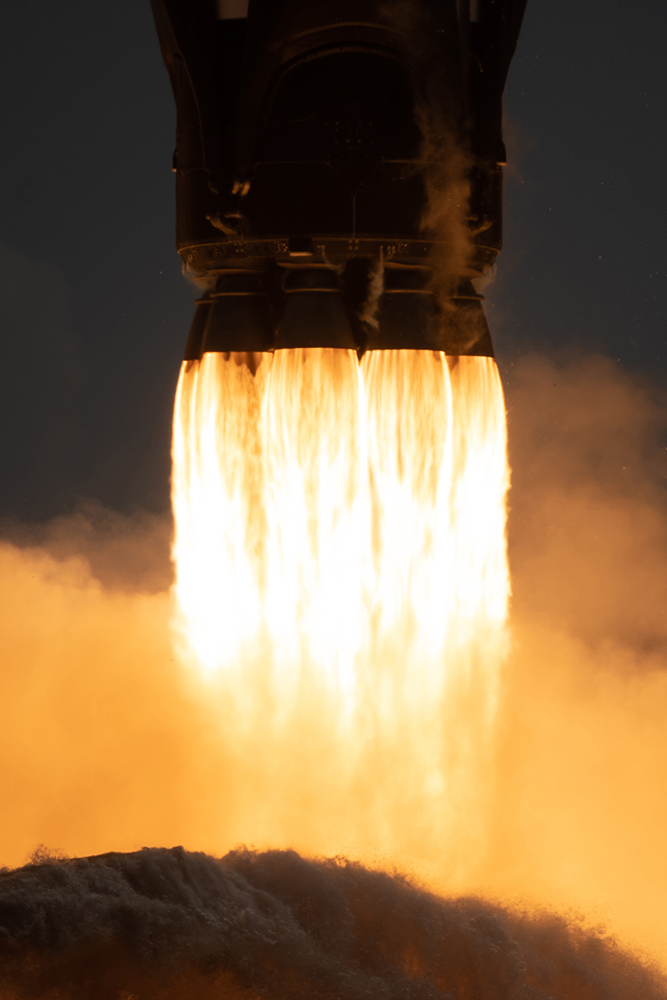
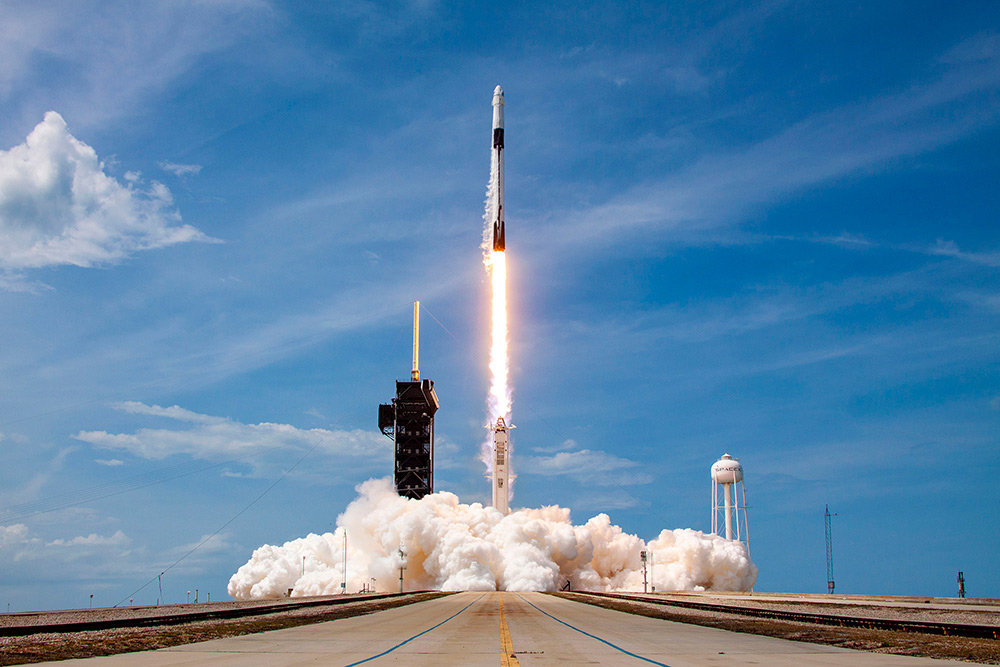





 任務(wù)期間,,機組人員和SpaceX任務(wù)控制器將驗證航天器的環(huán)境控制系統(tǒng),、顯示和控制系統(tǒng)、機動推進器和自動對接能力等的性能,。圖片來源:Bill Ingalls/NASA
任務(wù)期間,,機組人員和SpaceX任務(wù)控制器將驗證航天器的環(huán)境控制系統(tǒng),、顯示和控制系統(tǒng)、機動推進器和自動對接能力等的性能,。圖片來源:Bill Ingalls/NASA
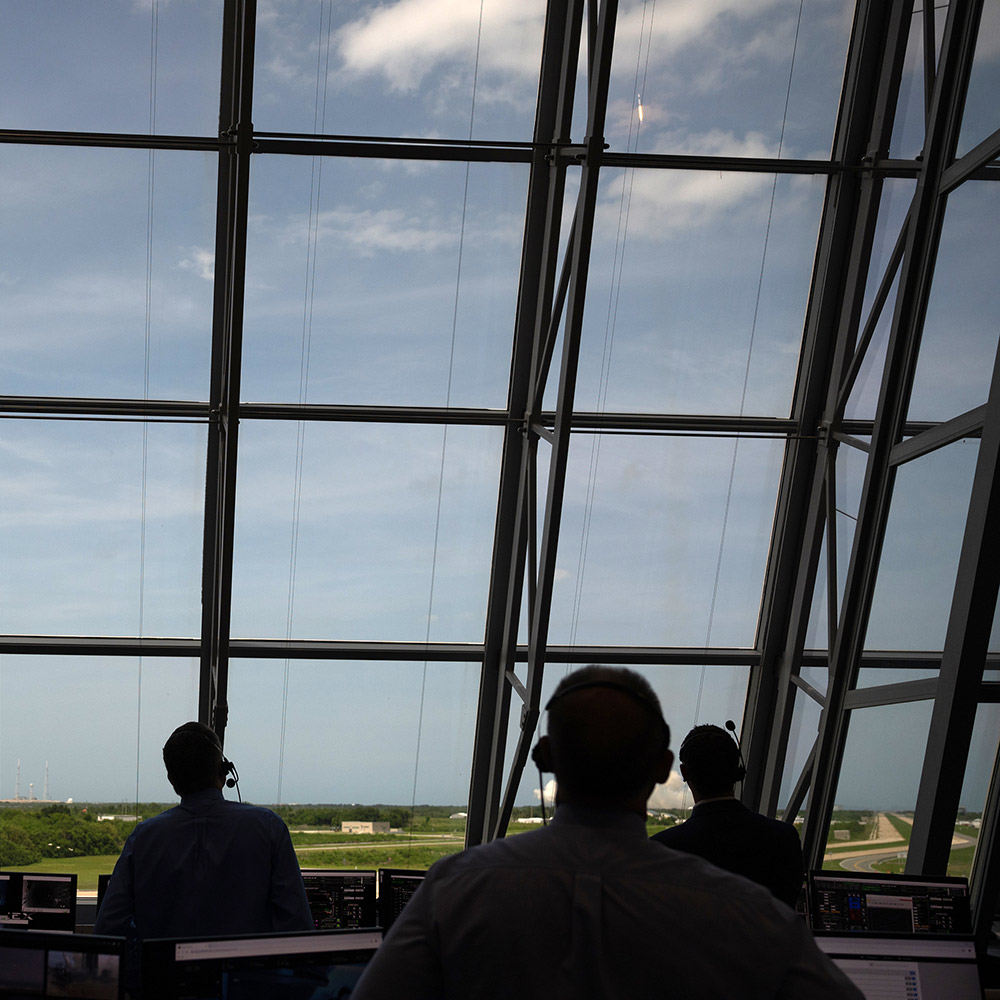 NASA和SpaceX工作組在佛羅里達州肯尼迪航天中心的發(fā)射控制中心監(jiān)控SpaceX獵鷹9號火箭的發(fā)射,。圖片來源:Joel Kowsky/NASA
NASA和SpaceX工作組在佛羅里達州肯尼迪航天中心的發(fā)射控制中心監(jiān)控SpaceX獵鷹9號火箭的發(fā)射,。圖片來源:Joel Kowsky/NASA  載人龍飛船的機組人員對國際空間站進行長達19小時的追蹤。圖片來源:Joe Burbank—Orlando Sentinel/Tribune News Service via Getty Images
載人龍飛船的機組人員對國際空間站進行長達19小時的追蹤。圖片來源:Joe Burbank—Orlando Sentinel/Tribune News Service via Getty Images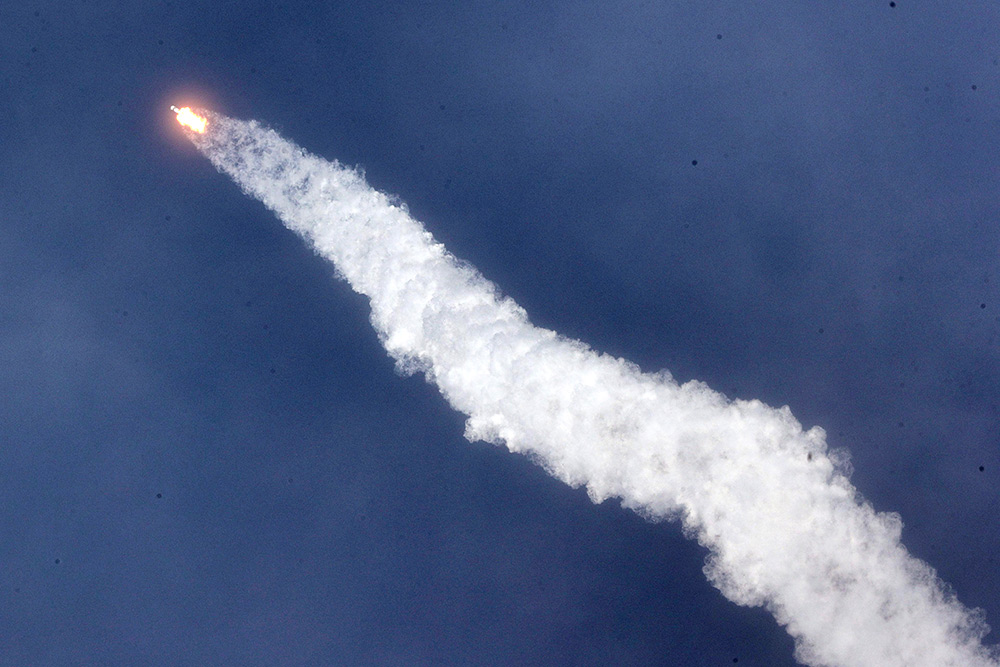  據(jù)NASA稱,,獵鷹火箭第一級的9臺梅林發(fā)動機,,產(chǎn)生超過170萬磅推力(775噸推力)。圖片來源:Joe Burbank—Orlando Sentinel/Tribune News Service via Getty Images
據(jù)NASA稱,,獵鷹火箭第一級的9臺梅林發(fā)動機,,產(chǎn)生超過170萬磅推力(775噸推力)。圖片來源:Joe Burbank—Orlando Sentinel/Tribune News Service via Getty Images 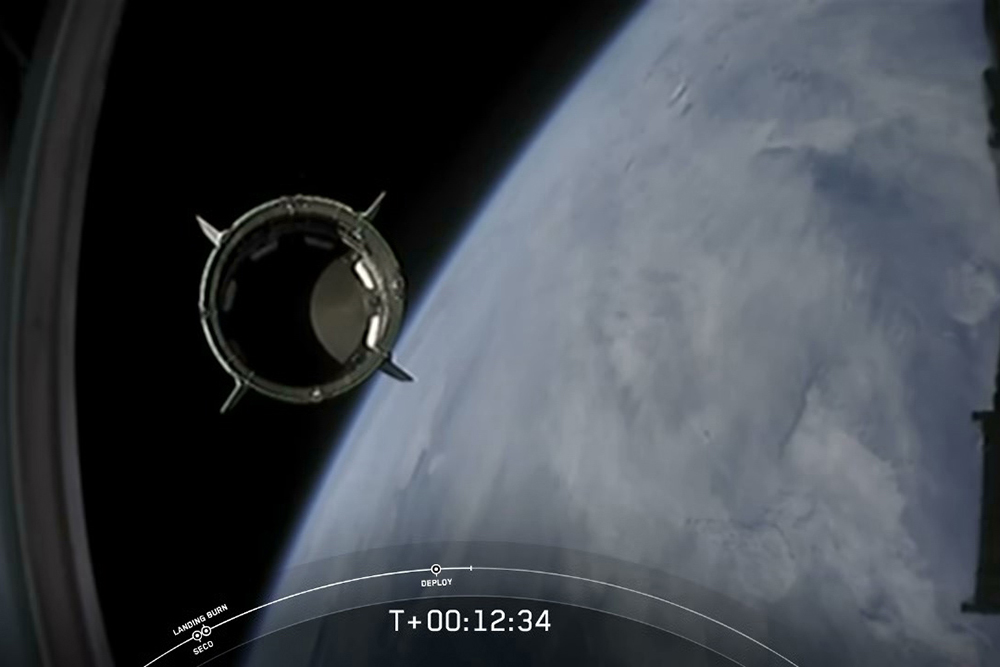 SpaceX的龍飛船與獵鷹9號火箭的第二級助推器分離,。圖片來源:NASA TV
SpaceX的龍飛船與獵鷹9號火箭的第二級助推器分離,。圖片來源:NASA TV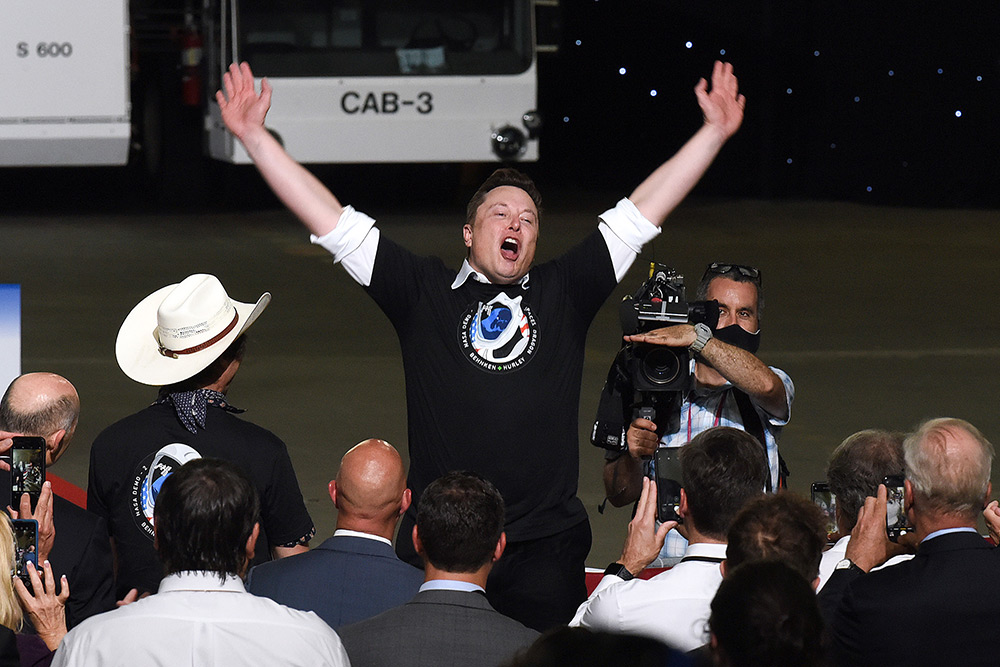  SpaceX的首席執(zhí)行官埃隆?馬斯克慶祝獵鷹9號火箭發(fā)射成功,,這也標志著美國商業(yè)載人航天時代的到來。圖片來源:Paul Hennessy—SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images
SpaceX的首席執(zhí)行官埃隆?馬斯克慶祝獵鷹9號火箭發(fā)射成功,,這也標志著美國商業(yè)載人航天時代的到來。圖片來源:Paul Hennessy—SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images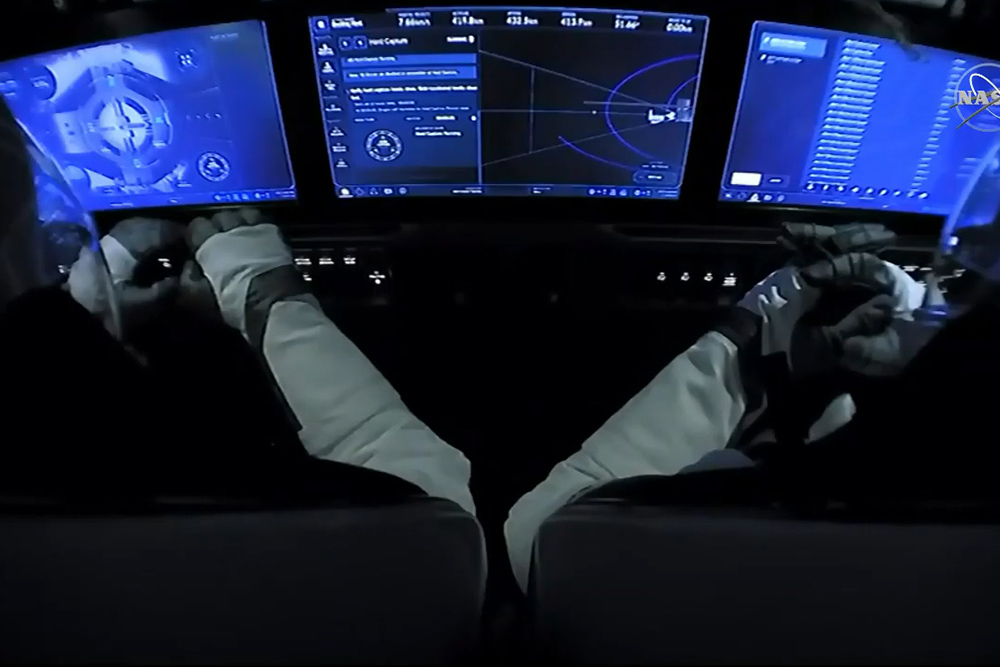  2020年5月31日,,NASA的SpaceX Demo-2宇航員在SpaceX 龍飛船內(nèi)通過顯示器監(jiān)查飛船與國際空間站的對接情況,。圖片來源:NASA TV
2020年5月31日,,NASA的SpaceX Demo-2宇航員在SpaceX 龍飛船內(nèi)通過顯示器監(jiān)查飛船與國際空間站的對接情況,。圖片來源:NASA TV

編譯:于佳鑫
上周六,,兩名美國宇航員搭載SpaceX的獵鷹9號火箭,,從佛羅里達州卡納維拉爾角發(fā)射,飛向國際空間站,。這是人類歷史上的首次商業(yè)載人航天發(fā)射,。
道格拉斯?赫爾利和羅伯特?本肯也是自2011年7月美國航天飛機退役后第一批從本土搭載國產(chǎn)火箭和飛船前往空間站的宇航員。
此次由美國國家航空航天局(NASA)出資支持的任務(wù)將啟動太空私有化的下一個主要階段,。未來將可能建造一個私人空間站,,并在地球以外創(chuàng)建私人任務(wù)。
美國東部時間上周日上午10點16分,,赫爾利和本肯抵達國際空間站,,并將航天器與空間站的端口對接。該飛船的對接機構(gòu)在飛越中國北部和蒙古時連接到該節(jié)點,。2014年,,美國宇航局委托兩家私營公司——航空巨頭波音公司和埃隆?馬斯克領(lǐng)導的SpaceX公司,制造能夠?qū)⑷祟愡\送到國際空間站的運載工具。從某種程度上說,,波音公司落后于其競爭對手SpaceX,,但如果能解決星際飛船艙的故障問題,它的首次飛行任務(wù)預計將在明年完成,。
下面讓我們通過照片,,感受這個歷史上的里程碑時刻。(財富中文網(wǎng))
編譯:于佳鑫
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on last Saturday carrying two astronauts to the International Space Station, marking the first-ever commercial launch of humans into orbit.
Astronauts Douglas Hurley and Robert Behnken are also the first people to lift off into orbit from the United States since the last space shuttle flight in July 2011.
The mission, paid for by NASA, is expected to kick off the next major phase in the privatization of space, which has so far focused on satellite launches. Plans include the launch of private astronauts, the construction of a private space station, and possibly the creation of private missions beyond Earth.
Hurley and Behnken arrived at the ISS’s Harmony port on Sunday, docking at 10:16 a.m. EDT while the spacecraft was flying about 262 miles above the northern border of China and Mongolia. In 2014, NASA commissioned Elon Musk–led SpaceX and aerospace giant Boeing to build launch vehicles capable of carrying humans to the station. Boeing has fallen somewhat behind its rival, with its first mission expected next year if it can work out glitches with its Starliner capsule.
Scroll below to see the historic mission through photos.
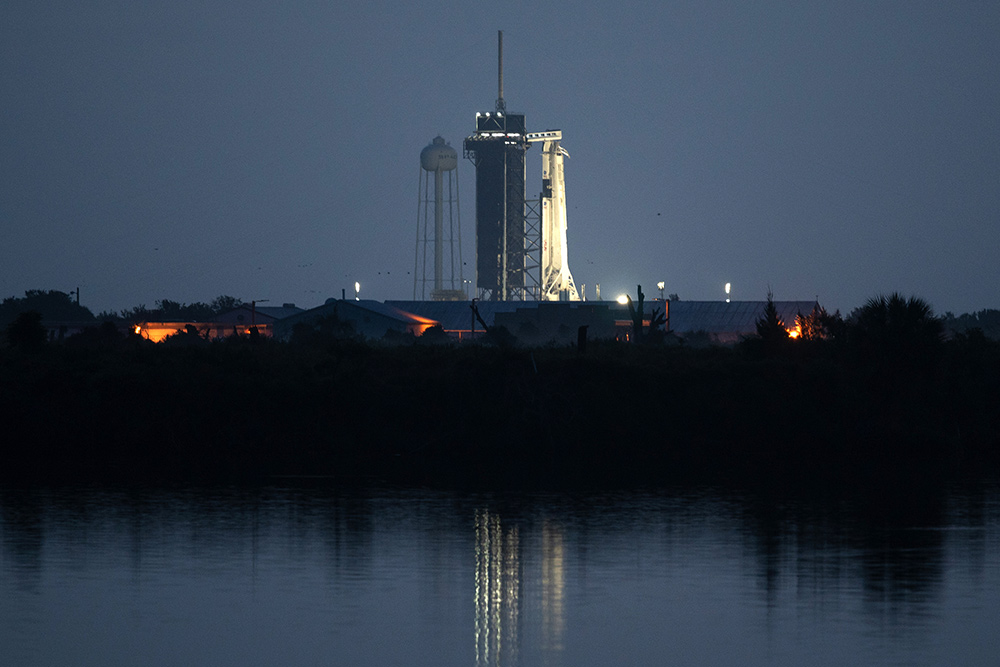
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft on board is illuminated on the launchpad at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission, May 30, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
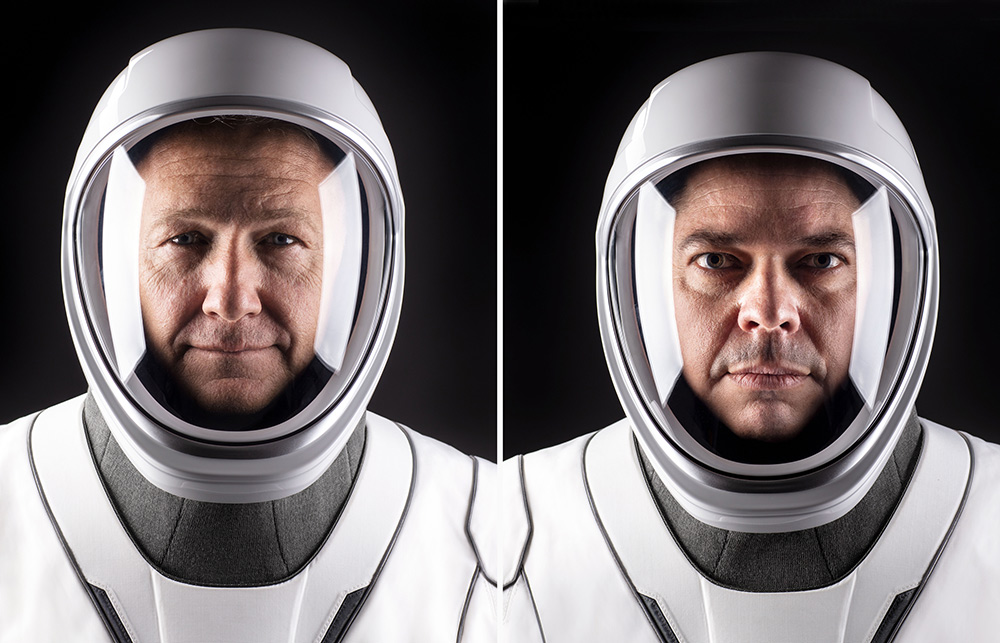
Astronauts Douglas Hurley (left) and Robert Behnken
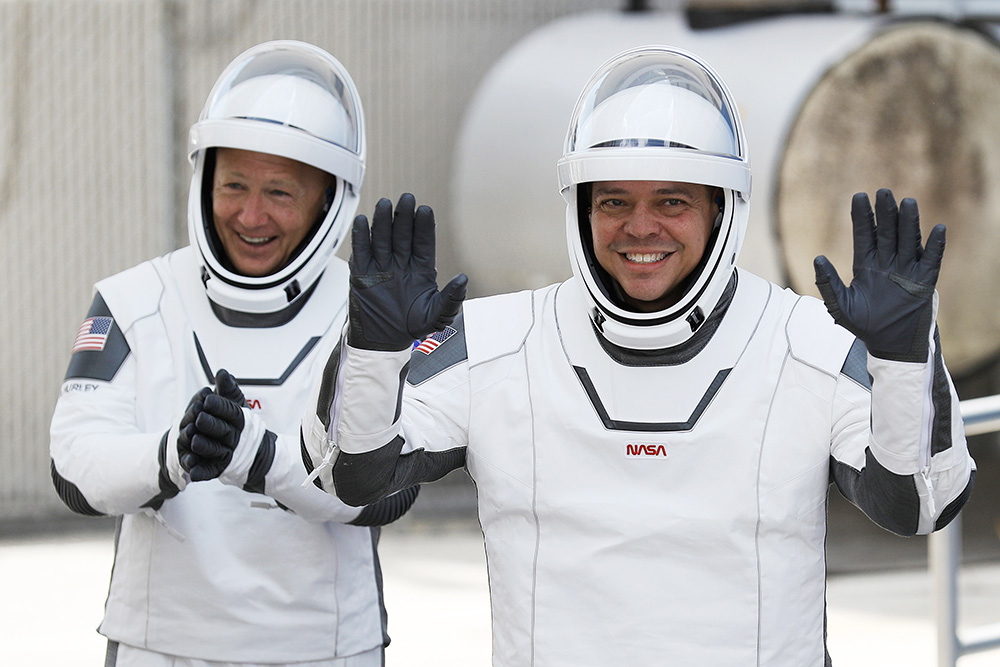
NASA astronauts Doug Hurley (left) and Bob Behnken emerge from the Operations and Checkout Building on their way to the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft.
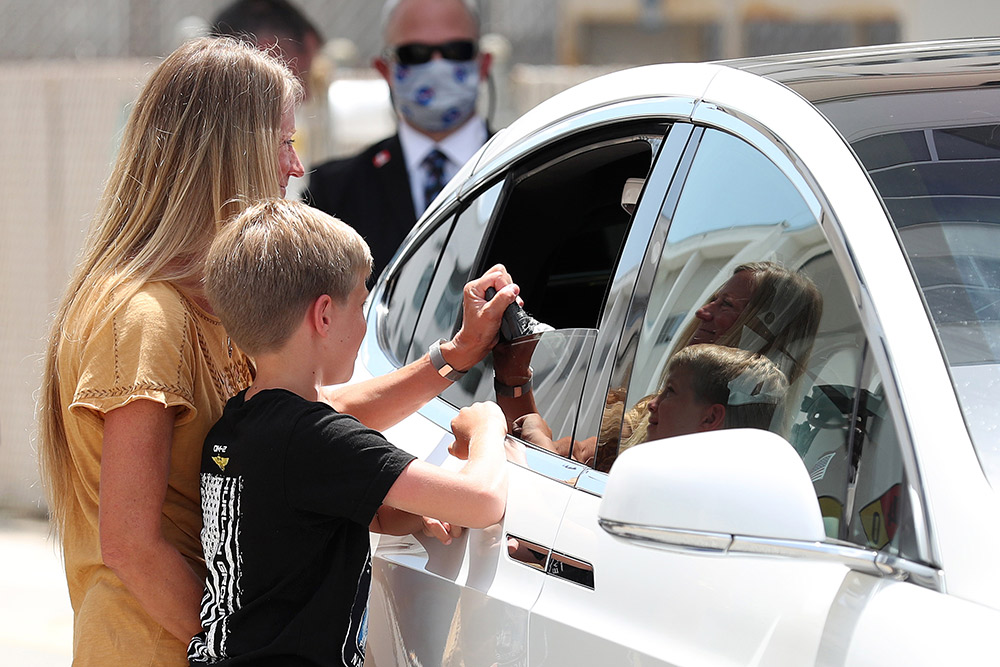
Sitting in a Tesla, NASA astronaut Doug Hurley says goodbye to his wife, Karen Nyberg, and son, Jack, after leaving the Operations and Checkout Building and heading for the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
The successful takeoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, marking a new era in human spaceflight as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from U.S. soil to low Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011.
The Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
During the mission, the crew and SpaceX mission controllers will verify the performance of the spacecraft’s environmental control system, displays and control system, maneuvering thrusters, autonomous docking capability, and more.
NASA and SpaceX teams monitor the launch of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
The Crew Dragon embarks on its 19-hour pursuit of the International Space Station.
According to NASA, the nine Merlin engines on the Falcon rocket’s first stage generate more than 1.7 million pounds of thrust as the vehicle climbs away from Florida’s Space Coast. At about one minute into the flight, the rocket passed through Max Q, the point of peak mechanical stress.
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft separates from the second stage of the Falcon 9 rocket.
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk celebrates the successful launch of a Falcon 9 rocket, marking the start of the commercial crew era of U.S. human spaceflight.
NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 crew members monitor their displays inside the SpaceX Crew Dragon during docking operations at the International Space Station on May 31, 2020.
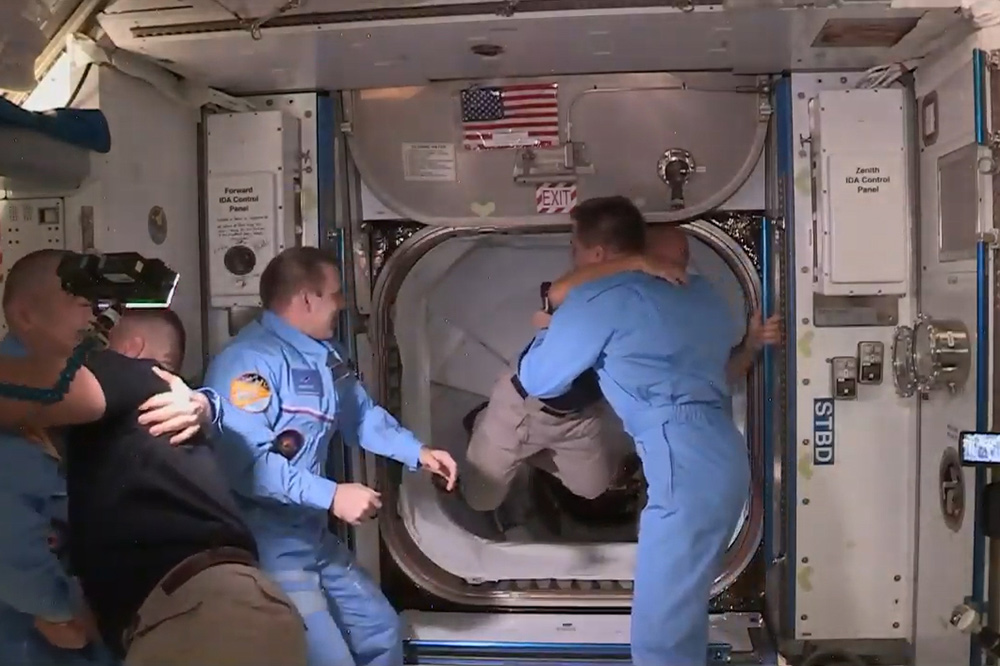
NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 crew members Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are greeted by Expedition 63 crew members Chris Cassidy, Ivan Vagner, and Anatoly Ivanishin at the International Space Station on May 31, 2020.






